- Language:English
- English
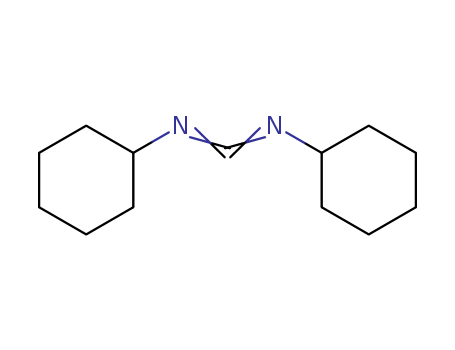

CasNo: 538-75-0
Molecular Formula: C13H22N2
Appearance: colorless solid
|
Description |
Dicydohexyl carbodiimide is used in peptide chemistry as a coupling reagent. It is both an irritant and a sensitizer, and caused contact dermatitis in pharmacists and chemists. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Colorless solid |
|
Uses |
In the synthesis of peptides. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A carbodiimide compound having a cyclohexyl substituent on both nitrogen atoms. |
|
Preparation |
A stirred mixture of N,N′-dicyclohexylurea (19.7 g), phosphorus pentoxide (100 g), sand (175 g), and pyridine (700 mL) was refluxed for 2.25 h. Stirring was no longer possible after about 30 min. The mixture was filtered and the residue was extracted with pyridine (100 mL). Pyridine was removed from the combined solutions on a flash evaporator, and the residual oil was extracted with boiling petroleum ether (bp 60–80 C°) (2 × 100 mL), and then with diethyl ether (100 mL). The combined extracts were washed with iced water (3×80 mL), dried over calcium chloride, and filtered. The solvents were removed from the filtrate under reduced pressure to give 17.4 g of an oil, which on distillation yielded 13.7 g (76%) of a clear liquid; bp 143 C° (3.5 mmHg), which solidified in the receiver; mp 34–35 C°. Another method for producing DCC from dicyclohexylurea is a two-step process using phosphoryl chloride in dichloromethane at 40 C° for 4 h under non-basic conditions followed by removal of acidic components with aq. sodium hydroxide. This method, which gives an 89% yield of DCC, has been presented in a patent application. |
|
General Description |
White crystalline solid with a heavy sweet odor. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Sensitive to moisture. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an imide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx). Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is incompatible with acids and oxidizing agents. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide reacts with water. |
|
Hazard |
A poison by skin contact. Moderately toxic by ingestion and inhalation. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is probably combustible. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
Contact allergens |
Used in peptide chemistry as a coupling reagent. It is both an irritant and a sensitizer and has caused contact dermatitis in pharmacists and chemists. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Laboratory reagent |
|
Shipping |
UN2928 Toxic solids, corrosive, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, 8- Corrosive material, Technical Name Required. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1- Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required |
|
Purification Methods |
It is sampled as a liquid after melting in warm H2O. It is sensitive to air, and it is a potent skin irritant. It can be distilled in a vacuum and is best stored in a tightly stoppered flask in a freezer. It is very soluble in CH2Cl2 and pyridine where the reaction product with H2O, after condensation, is dicyclohexyl urea which is insoluble and can be filtered off. Alternatively dissolve it in CH2Cl2, add powdered anhydrous MgSO4, shake for 4hours, filter, evaporate and distil at 0.6mm pressure and oil bath temperature of 145o. [Bodansky et al. Biochemical Preparations 10, 122 1963, Schmidt & Seefelder Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 571 83 1951, Schmidt et al. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 612 11 1958, Beilstein 12 IV 72.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
Dust may for explosive mixture with air. Reacts with steam and water. N,N0 - Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an amine/imide: contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire and explosions. Incompatible with acids, strong bases, strong reducing agents (may form flammable gasses); azo and diazo compounds (may form toxic gases); chlorinated hydrocarbons; nitro compounds. Contact with mixture of acetic acid 1 dinitrogen trioxide may cause explosion. The combustion of amide compounds generate nitrogen oxides (NOx). In the presence of moisture, may attack metals and plastics. |
|
Waste Disposal |
Whatever cannot be saved for recovery or recycling should be managed in an appropriate and approved waste facility. Although not a listed RCRA hazardous waste, this material may exhibit one or more characteristics of a hazardous waste and require appropriate analysis to determine specific disposal requirements. Processing, use or contamination of this product may change the waste management options. State and local disposal regulations may differ from federal disposal regulations. Dispose of container and unused contents in accordance with federal, state and local requirements |
This work describes the reversible C-add...
Reactions of 3-imino-azaphosphiridine co...
The invention discloses a preparation me...
The invention relates to the technical f...
The invention discloses a method for pre...
The invention relates to a method for pr...
N,N'-Dicyclohexyl-C-chlor-formamidinium

dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium hydroxide;
In
water;
|
92.4% |
Cyclohexyl isocyanide
cyclohexylamine

1,3-Dicyclohexylurea


dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
oxygen; sodium carbonate;
palladium diacetate;
In
acetonitrile;
at 100 ℃;
for 3h;
under 2068.6 Torr;
|
35% 10 % Chromat. |
Cyclohexyl isocyanate
3-methyl-1-phenylphospholane

1,3-Dicyclohexylurea
p-toluenesulfonyl chloride
4-hydroxymethyl-2-oxo-2λ5-[1,3,2]dioxaphospholan-2-ol
3-cyclohexyl-2-cyclohexylimino-6-methyl-2,3-dihydro-[1,3]oxazin-4-one
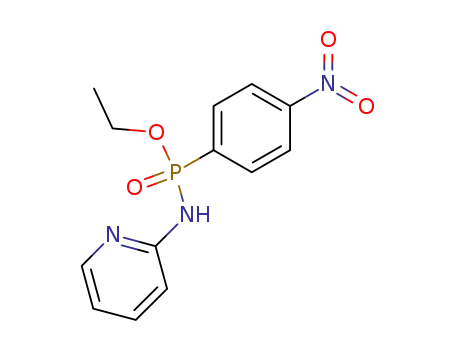
(4-nitro-phenyl)-phosphonic acid ethyl ester-[2]pyridylamide
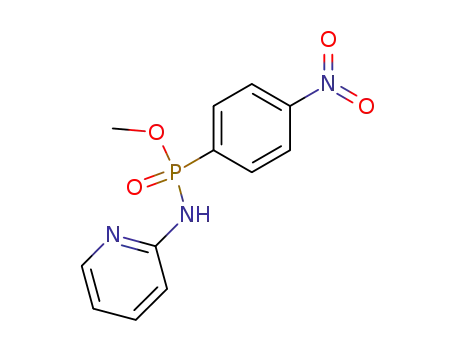
(4-nitro-phenyl)-phosphonic acid methyl ester-[2]pyridylamide
CAS:138071-82-6
CAS:38083-17-9
CAS:26198-19-6
CAS:82911-69-1