- Language:English
- English
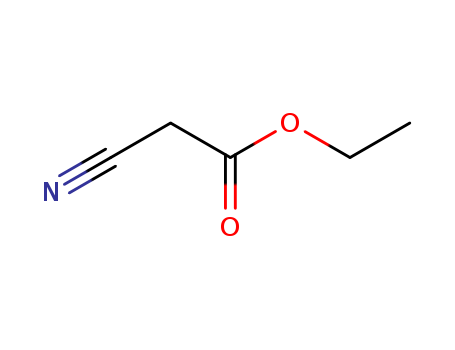

CasNo: 105-56-6
Molecular Formula: C5H7NO2
Appearance: Clear to very yellow liquid
|
Preparation |
Ethyl cyanoacetate can be prepared by the action of sodium or potassium cyanide on ethyl chloroacetate, and by the action of sodium cyanide on sodium chloroacetate, followed by esterification. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Slightly soluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Ethyl cyanoacetate is both a nitrile and an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Nitriles may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids. |
|
Hazard |
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. |
|
Health Hazard |
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors, dusts or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Reaction with water or moist air will release toxic, corrosive or flammable gases. Reaction with water may generate much heat that will increase the concentration of fumes in the air. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. Substance will react with water (some violently) releasing flammable, toxic or corrosive gases and runoff. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water. |
|
Safety Profile |
oison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal and subcutaneous routes. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidzing materials. Wdl react with water or steam to produce toxic and flammable vapors. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition or on contact with acid or acid fumes it emits highly toxic fumes of CN-. See also NITRILES. |
|
Potential Exposure |
A nitrile used to manufacture dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals. |
|
Purification Methods |
Shake the ester several times with aqueous 10% Na2CO3, wash it well with water, dry with Na2SO4 and fractionally distil it. [Beilstein 2 IV 1889.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, and reducing agents. Nitriles may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids. Reacts with moisture, water, and steam, forming toxic fumes. |
|
Waste Disposal |
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. |
|
General Description |
Ethyl cyanoacetate is a versatile chemical intermediate used in multicomponent reactions for synthesizing biologically active compounds, including antimicrobial pyrimidinones, N-arylquinolines, and antimalarial or anticancer derivatives. It serves as a key reactant in microwave-mediated and DBU-catalyzed reactions due to its active methylene group, enabling efficient, high-yield syntheses under eco-friendly conditions. Additionally, it participates in thermal cyclization and SRN1 reactions for constructing heteroaromatic scaffolds, highlighting its utility in pharmaceutical and synthetic chemistry. |
InChI:InChI:1S/C5H7NO2/c1-2-8-5(7)3-4-6/h2-3H2,1H3
A series of novel semi-squaraine sensiti...
The treatment of 2-iminothieno[3,2-α]ind...
-
-
The methods of 1H and 13C NMR and UV spe...
A novel radical-mediated trifunctionaliz...
This invention relates to a process for ...
This invention relates to a process for ...
This invention relates to a process for ...
2,2'-dicyano-3,3'-dioxo-3,3'-p-phenylene-di-propionic acid diethyl ester

water

terephthalic acid

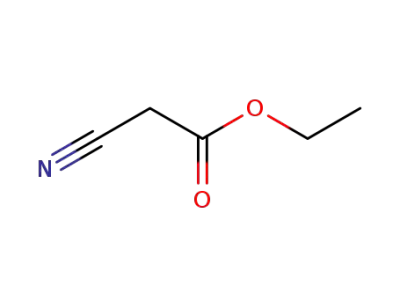
ethyl 2-cyanoacetate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|

ethyl benzylidenecyanoacetate

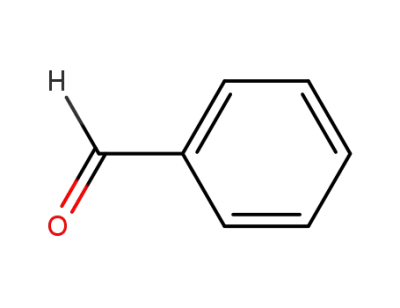
benzaldehyde


ethyl 2-cyanoacetate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
solid form;
|
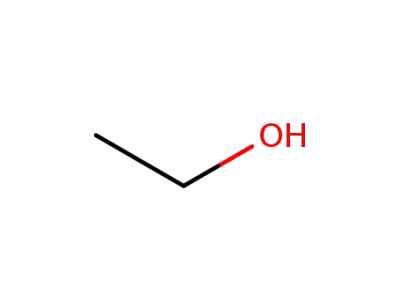
ethanol

cyanoacetic acid
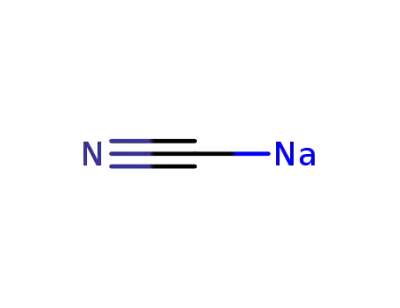
sodium cyanide

chloroacetic acid ethyl ester
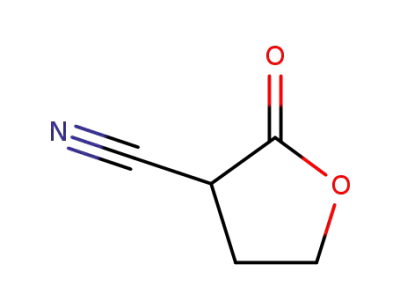
2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-carbonitrile
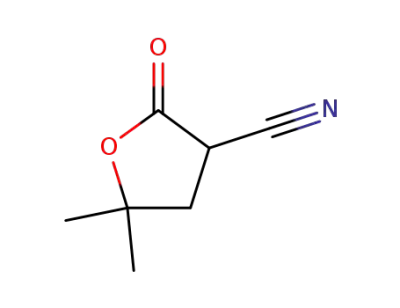
α-cyano-γ,γ-dimethyl-γ-butyrolactone
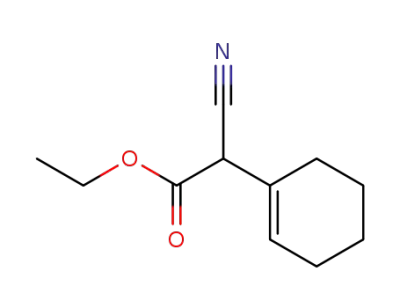
ethyl 1-cyclohexenylcyanoacetate
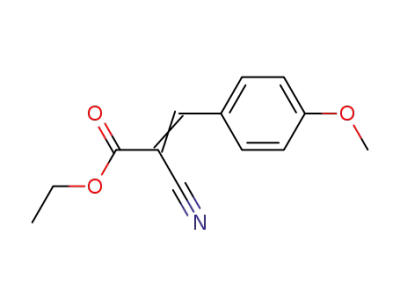
ethyl 2-cyano-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate
CAS:138071-82-6
CAS:38083-17-9
CAS:32222-06-3
CAS:5466-77-3